When it comes to construction, waterproofing, and roofing solutions, the materials chosen play a vital role in durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Among modern innovations, fiberglass membrane has emerged as a strong contender against traditional materials like asphalt felt, bitumen sheets, and tar paper. Each option has its strengths and weaknesses, but as the construction industry moves toward efficiency and sustainability, fiberglass membrane is gaining more attention. This article explores the differences, benefits, and drawbacks of fiberglass membrane compared to conventional materials, helping builders, contractors, and property owners make informed decisions.
Understanding Fiberglass Membrane
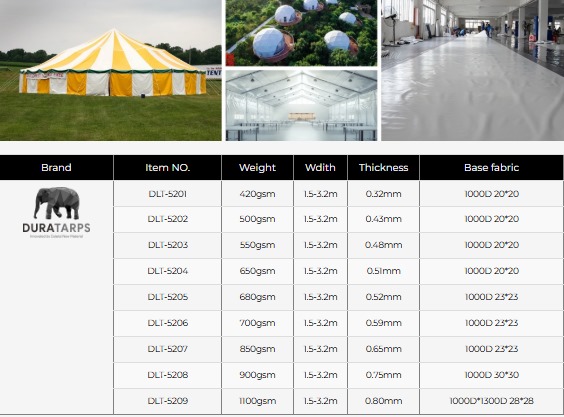
Fiberglass membrane is a lightweight yet durable reinforcement material made from woven or non-woven fiberglass strands. It is commonly used in waterproofing systems, roofing, flooring, and wall reinforcements. Known for its excellent tensile strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability, fiberglass membrane offers a modern alternative to traditional felt-based or bitumen-based products. Unlike organic materials that may decompose over time, fiberglass membrane is resistant to rot, mold, and environmental degradation, making it a long-lasting solution in demanding conditions.
Traditional Materials in Construction
Before fiberglass membrane became widely available, traditional materials such as asphalt felt, tar paper, and bitumen sheets dominated the industry. These materials are made primarily from organic fibers or paper saturated with bitumen or asphalt. While affordable and easy to install, they have limitations in terms of resistance to extreme weather, fire hazards, and overall durability. Traditional options often require frequent maintenance or replacement, increasing long-term costs despite their lower upfront price.
Key Differences Between Fiberglass Membrane and Traditional Materials
Strength and Durability
Fiberglass membrane offers significantly higher tensile strength compared to asphalt felt or tar paper. This means it can withstand stretching, tearing, and impact better than traditional materials. In contrast, felt-based products can weaken when exposed to moisture over long periods, leading to premature failure. For structures exposed to harsh climates, fiberglass membrane provides a more reliable and long-lasting solution.
Resistance to Moisture and Mold
One of the most notable advantages of fiberglass membrane is its resistance to water absorption. Traditional felt or paper materials tend to absorb water, which can cause swelling, warping, or mold growth. This makes them less reliable in humid or rainy environments. Fiberglass membrane, being non-organic, does not absorb water and effectively prevents mold or rot, making it ideal for waterproofing applications.
Thermal and Fire Resistance
Fiberglass has natural fire-resistant properties, withstanding higher temperatures without losing its structure. Traditional bitumen-based sheets, however, can soften, melt, or even ignite under extreme heat. This makes fiberglass membrane a safer choice, particularly in areas prone to high temperatures or fire hazards.
Longevity and Maintenance
Fiberglass membrane is designed to last longer than traditional alternatives. Its resistance to weathering, UV rays, and chemical exposure extends its lifespan significantly. In contrast, asphalt felt and similar materials often require replacement every few years, particularly in demanding climates. The reduced need for frequent repairs or replacements gives fiberglass membrane an edge in long-term cost efficiency.
Ease of Installation
Both fiberglass membrane and traditional materials are relatively easy to install, but fiberglass membrane is lighter in weight and more flexible. Contractors find it easier to handle, cut, and lay, which can reduce labor time. Traditional materials, though familiar and widely available, can be bulkier and harder to manipulate, particularly in complex roofing systems.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability has become an important factor in construction decisions. Traditional asphalt-based products are petroleum-derived and not biodegradable, contributing to environmental concerns. Fiberglass membrane, while also synthetic, tends to last much longer, reducing the frequency of disposal. Additionally, many fiberglass products can be manufactured with energy-efficient methods, giving them a smaller overall carbon footprint compared to traditional bitumen products.
Applications of Fiberglass Membrane
Fiberglass membrane is versatile and used in a variety of applications:
- Roofing reinforcement: Provides an extra layer of strength to waterproofing membranes, preventing cracks and leaks.
- Wall and floor waterproofing: Ensures moisture resistance in bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
- Industrial uses: Used in pipelines, tanks, and insulation due to its resistance to chemicals and heat.
- Construction reinforcements: Acts as a stabilizing layer in cement and plaster systems, reducing the risk of shrinkage cracks.
These diverse applications showcase how fiberglass membrane is not just a roofing solution but an adaptable material for modern construction needs.
Cost Comparison
At first glance, traditional materials are usually cheaper upfront than fiberglass membrane. Asphalt felt, tar paper, and bitumen sheets are widely available and affordable, making them attractive for budget-conscious projects. However, when long-term costs are considered, fiberglass membrane often proves more economical. Its durability, lower maintenance requirements, and extended lifespan mean fewer replacements and reduced labor costs over time. For property owners and contractors looking at the bigger picture, fiberglass membrane offers better value despite the higher initial price.
Advantages of Fiberglass Membrane Over Traditional Materials
- Superior tensile strength and flexibility
- Excellent resistance to water, mold, and rot
- Fire and heat resistance for added safety
- Longer lifespan with reduced maintenance needs
- Lightweight and easier to install
- More environmentally friendly over the long term
When Traditional Materials Might Still Be Preferred
Despite the many advantages of fiberglass membrane, traditional materials still have a place in construction. For small projects, temporary structures, or low-budget builds, asphalt felt and similar products remain popular due to their affordability. In regions where advanced materials are less accessible, contractors may also prefer conventional options simply for ease of sourcing. Additionally, some traditional products may perform adequately in mild climates where durability and weather resistance are less critical.
The Future of Construction Materials
As construction technology advances, the industry is moving toward materials that balance performance, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Fiberglass membrane represents this shift, offering improved durability and eco-friendly features compared to outdated methods. With growing emphasis on green building practices and lifecycle cost analysis, fiberglass membrane is likely to become the standard in many applications, gradually replacing traditional alternatives.
Conclusion
The choice between fiberglass membrane and traditional materials ultimately depends on project requirements, budget, and long-term goals. For those seeking durability, resistance to environmental challenges, and reduced maintenance, fiberglass membrane clearly stands out as the superior choice. While traditional materials may still be viable for certain low-cost or temporary applications, the advantages of fiberglass membrane make it the better option for modern, sustainable, and long-lasting construction projects. By investing in fiberglass membrane, builders and property owners can ensure greater protection, safety, and value for years to come.